
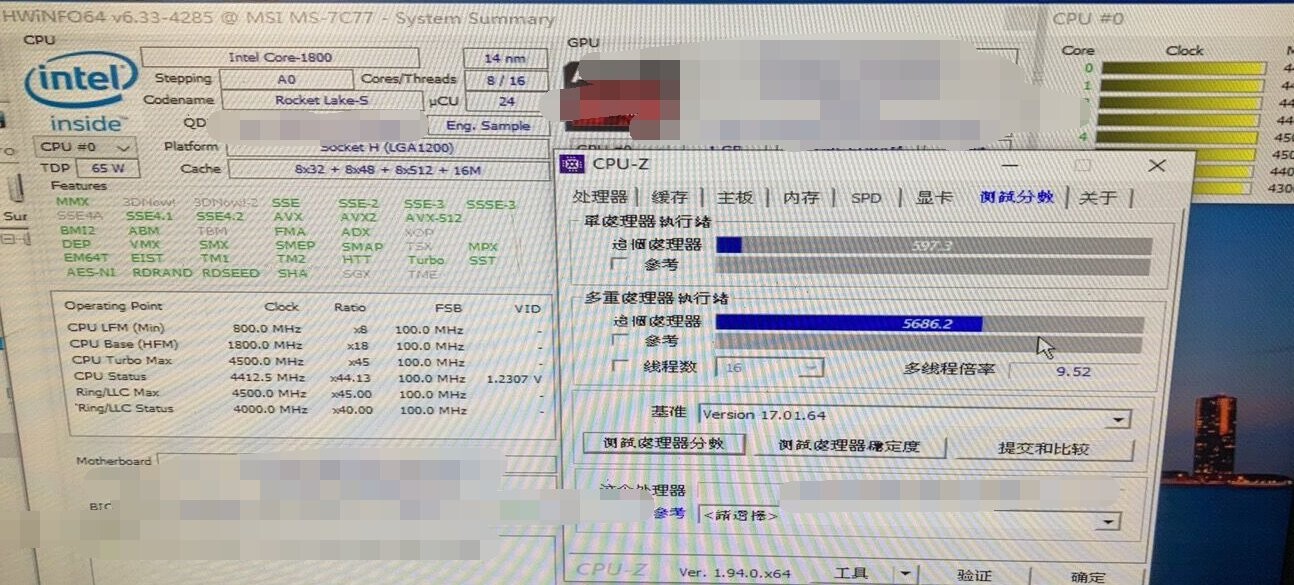
Here’s a table of the maximum CPUID input values the operating system will obtain from Intel processors when CPUID is executed with the EAX register set to 0. You should only enable it if you intend to use a newer processor with an operating system that does not support it. It is recommended that you leave it at the default setting of Disabled. When disabled, the processor will return the actual maximum CPUID input value of the processor when queried. When enabled, the processor will limit the maximum CPUID input value to 03h when queried, even if the processor supports a higher CPUID input value.

It allows you to circumvent problems with older operating systems that do not support newer processors with extended CPUID information. This is where the CPUID Maximum Value Limit BIOS feature comes in. However, if you attempt to use a new processor with an old operating system, that operating system may not be able to handle the extra CPUID information provided by the processor. The maximum CPUID input value determines the values that the operating system can write to the CPUID’s EAX register to obtain information about the processor.

This determines the kind of basic information CPUID can provide the operating system. The first step is to query the processor to find out the highest input value CPUID recognises, by executing CPUID with the EAX register set to 0. When the computer is booted up, the operating system executes the CPUID instruction to identify the processor and its capabilities.
Quick Review of CPUID Maximum Value Limit


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
